Contents
Fats have long been demonized in the realm of nutrition, often being associated with weight gain and health issues. However, not all fats are created equal, and it’s essential to distinguish between healthy and unhealthy fats.
Among the various types of fats, essential fats play a vital role in maintaining overall health and well-being.
In this article, we will delve into the world of essential fats, exploring their significance and providing examples of foods rich in these vital nutrients.
What Are Essential Fats?
Essential fats, also known as essential fatty acids (EFAs), are specific types of fats that the human body cannot produce on its own.
Consequently, they must be obtained through dietary sources. The two primary categories of essential fats are omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. These fatty acids serve as building blocks for various critical functions within the body.
Omega-3 fatty acids are renowned for their anti-inflammatory properties and are crucial for the normal development and functioning of the brain and nervous system. They play a role in reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, arthritis, and certain types of cancer [1].
On the other hand, omega-6 fatty acids, while also essential, need to be consumed in balance with omega-3s. They are involved in processes like blood clotting and immune system responses.
Molecular Makeup of Essential Fatty Acids
Essential fatty acids belong to the polyunsaturated fat category, which means they have multiple double bonds in their carbon chain. These double bonds are responsible for their unique chemical structure and biological functions.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
One of the two main categories of essential fatty acids, omega-3 fatty acids, are characterized by a specific structural feature.
They have their first double bond three carbon atoms away from the methyl end (the end of the carbon chain without the carboxyl group).
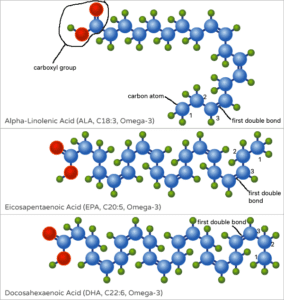
The most prominent omega-3 fatty acids include:
- Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA): ALA is a short-chain omega-3 fatty acid with 18 carbon atoms and three double bonds. It is typically found in plant-based sources such as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts.
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA): EPA is a long-chain omega-3 fatty acid with 20 carbon atoms and five double bonds. It is primarily found in marine sources, particularly fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines.
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA): DHA is another long-chain omega-3 fatty acid, also with 22 carbon atoms and six double bonds. It is abundant in fatty fish and is a critical structural component of cell membranes in the brain and retina.
Omega-6 Fatty Acids
The second category of essential fatty acids, omega-6 fatty acids, have their first double bond six carbon atoms away from the methyl end.
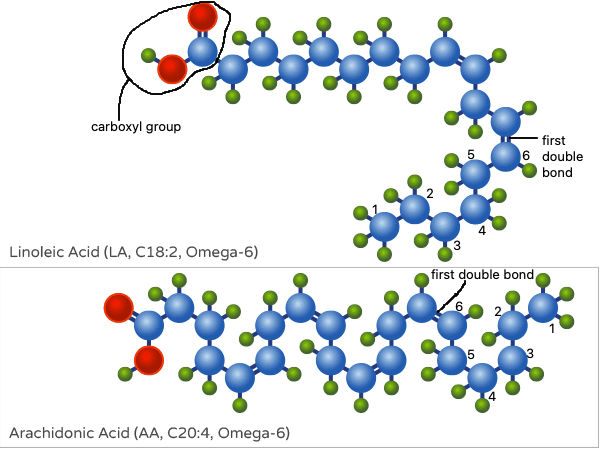
The most well-known omega-6 fatty acid is:
- Linoleic acid (LA): Linoleic acid is an 18-carbon omega-6 fatty acid with two double bonds. It is found in various plant-based sources, including vegetable oils (such as soybean and sunflower oil), nuts, and seeds.
Understanding the molecular structure of these essential fatty acids is crucial, as it directly influences their biological functions in the body.
Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids play diverse roles in various physiological processes, making them indispensable for overall health.
The Health Benefits of Essential Fats
- Heart Health: Omega-3 fatty acids, such as EPA and DHA, are incredibly beneficial for heart health. These fats have been demonstrated to lower blood pressure, reduce triglyceride levels, and decrease the risk of irregular heart rhythms. Consuming these fats in sufficient quantities can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Brain Function: DHA, a specific type of omega-3 fatty acid, is a major structural component of the brain. It is vital for cognitive function, memory, and overall brain health. Regular consumption of omega-3s has been associated with improved cognitive function, and some studies suggest it may help protect against age-related cognitive decline.
- Inflammation: Omega-3 fatty acids are well-regarded for their potent anti-inflammatory properties. Chronic inflammation is linked to a plethora of diseases, including diabetes, obesity, and autoimmune disorders. Omega-3s can help reduce inflammation throughout the body, mitigating the risk of these health issues.
- Skin Health: Essential fats are beneficial for maintaining healthy skin. They help prevent dryness and improve skin elasticity. Additionally, they can alleviate symptoms of skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis, making them a valuable addition to your diet for radiant, healthy skin.
- Hormone Regulation: Essential fats play a role in hormone production and function. An imbalance in essential fats can lead to hormonal issues, affecting various aspects of health, including menstrual cycles and fertility. Ensuring a proper intake of essential fats can help regulate hormonal functions in the body.
Dietary Sources of Essential Fats
Now, let’s explore a more detailed list of dietary sources of essential fats, along with their approximate essential fat content:
Foods High in Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Fatty Fish (Salmon, Mackerel, Trout, Sardines)




- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid) and DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid).
- Amount:
- Salmon (3.5 oz): Approximately 1.3 grams of combined EPA and DHA.
- Mackerel (3.5 oz): Roughly 4.5 grams of combined EPA and DHA.
- Trout (3.5 oz): About 0.8 grams of combined EPA and DHA.
- Sardines (3.5 oz): Contains roughly 2 grams of combined EPA and DHA.
Flaxseeds

- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: ALA (Alpha-linolenic Acid).
- Amount:
- One tablespoon of ground flaxseeds contains about 1.6 grams of ALA.
Chia Seeds

- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: ALA (Alpha-linolenic Acid).
- Amount:
- One tablespoon of chia seeds provides approximately 2.5 grams of ALA omega-3 fatty acids.
Walnuts

- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: ALA (Alpha-linolenic Acid).
- Amount:
- A quarter-cup of walnuts contains around 2.3 grams of ALA omega-3 fatty acids.
Hemp Seeds

- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: ALA (Alpha-linolenic Acid).
- Amount:
- One tablespoon of hemp seeds offers approximately 0.6 grams of ALA omega-3 and 2 grams of omega-6 fatty acids.
Foods High in Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Soybeans

- Omega-6 Fatty Acids: Primarily Linoleic Acid (LA).
- Amount:
- Half a cup of cooked soybeans provides approximately 2.2 grams of omega-6 fatty acids and 0.3 grams of ALA omega-3.
Pumpkin Seeds

- Omega-6 Fatty Acids: Linoleic Acid (LA).
- Amount:
- A quarter-cup of pumpkin seeds contains roughly 4 grams of omega-6 fatty acids.
Olive Oil

- Omega-6 Fatty Acids: Primarily Linoleic Acid (LA).
- Amount:
- One tablespoon of extra virgin olive oil has approximately 1.2 grams of monounsaturated fats.
Avocado

- Omega-6 Fatty Acids: Linoleic Acid (LA).
- Amount:
- A medium-sized avocado contains about 3.5 grams of omega-6 fatty acids and 0.5 grams of omega-3 fatty acids.
Edamame (Young Soybeans)

- Omega-6 Fatty Acids: Primarily Linoleic Acid (LA).
- Amount:
- Half a cup of shelled edamame provides approximately 2 grams of omega-6 fatty acids and 0.4 grams of ALA omega-3.
Conclusion
Essential fats, encompassing both omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, are critical for overall health.
They offer a wide range of health benefits, including heart health, brain function, inflammation reduction, skin health, and hormone regulation.
Ensuring a balance between these essential fats in your diet is key to promoting optimal well-being.
Incorporating foods rich in omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, such as fatty fish, seeds, nuts, and avocado, into your daily meals can help you maintain a balanced intake of these vital nutrients.
By doing so, you’ll be better equipped to experience the numerous health benefits essential fats provide, supporting a healthier and happier life.
Reference
[1] Omega-3 Fatty Acids: An Essential Contribution. The Nutrition Source, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. URL: https://nutritionsource.hsph.harvard.edu/what-should-you-eat/fats-and-cholesterol/types-of-fat/omega-3-fats/

